1. 최단 경로
: 정점 u와 정점 v가 연결되는 경로 중에서 간선들의 가중치 합이 최소가 되는 경로이다.
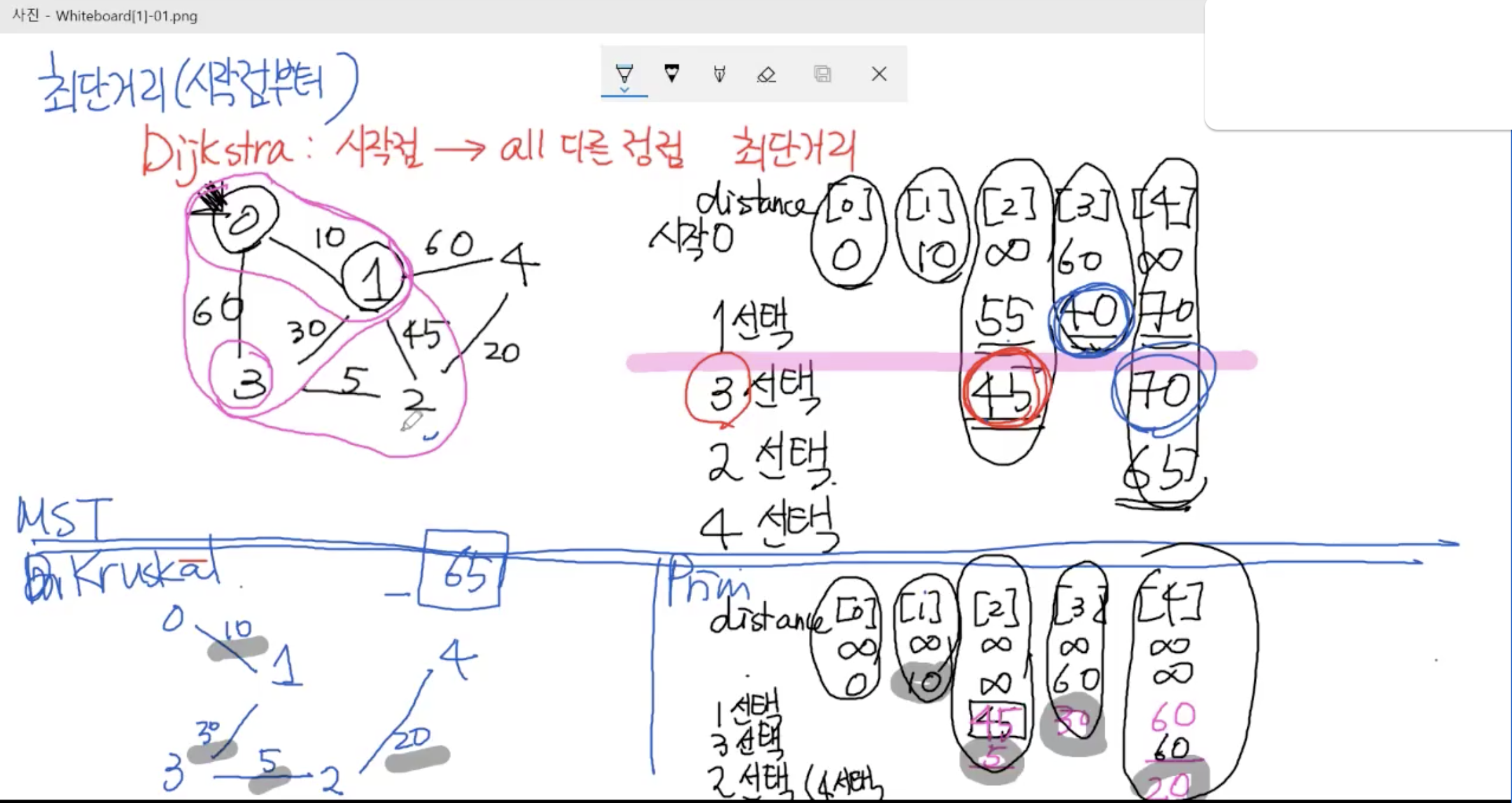
MST와 최단 경로의 차이
MST는 각 정점에 한 번씩 도달해야 하고, 총 비용은 가능한 모든 조합 중 최소여야 한다.
반면, 최단 경로는 가능한 최저 비용으로 시작 정점에서 목표 정점까지 도달하는 것이다.
알고리즘 -> 다익스트라, 플로이드
2. 다익스트라 알고리즘 - 최단경로
1) 동작 방식
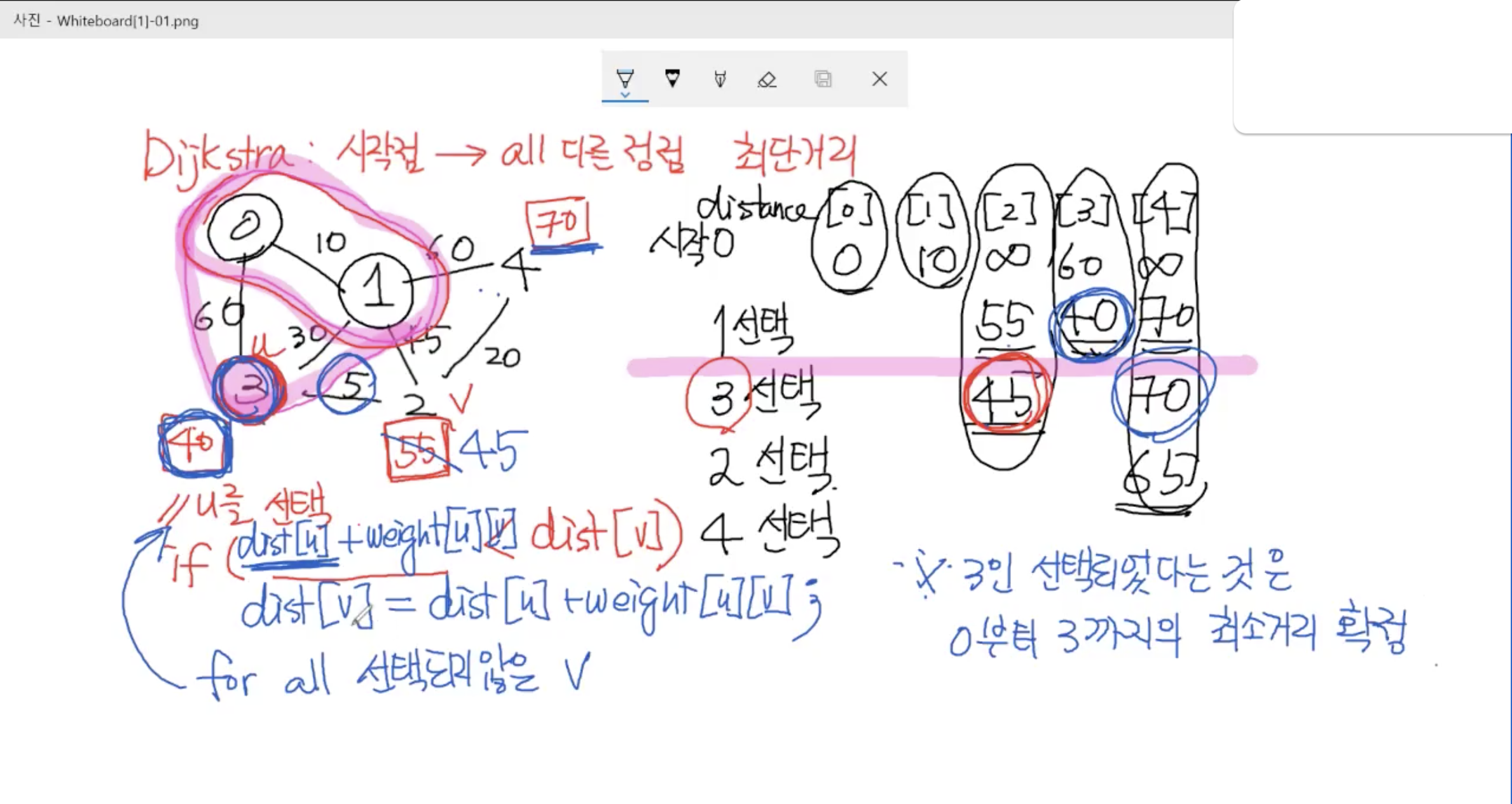
2) 핵심 코드
void shortest_path(GraphType* g, int start)
{
int i, u, w;
for (i = 0; i<g->n; i++) /* 초기화 */
{
distance[i] = g->weight[start][i];
found[i] = FALSE;
previous[i] = start;
}
found[start] = TRUE; /* 시작 정점 방문 표시 */
distance[start] = 0;
for (i = 0; i<g->n-1; i++) {
u = choose(distance, g->n, found);
found[u] = TRUE;
print_path(start, u);
printf("<%d>\n", distance[u]);
for (w = 0; w<g->n; w++){
if (!found[w]){
if (distance[u] + g->weight[u][w] < distance[w]){
distance[w] = distance[u] + g->weight[u][w];
previous[w] = u;
}
}
}
}
}
if (distance[u] + g->weight[u][w] < distance[w]){
distance[w] = distance[u] + g->weight[u][w];
previous[w] = u;
}
: (u까지의 거리와 u에서 w까지의 거리를 더한 것)이 (w까지의 총 거리)보다 적으면
(w까지의 총 거리)를 (u까지의 거리와 u에서 w까지의 거리를 더한 것)으로 변경한다.
3) 전체 코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAX_VERTICES 100
#define INF 1000000 /* 무한대 (연결이 없는 경우) */
typedef struct GraphType {
int n; // 정점의 개수
int weight[MAX_VERTICES][MAX_VERTICES];
} GraphType;
int distance[MAX_VERTICES];/* 시작정점으로부터의 최단경로 거리 */
int found[MAX_VERTICES]; /* 방문한 정점 표시 */
int previous[MAX_VERTICES];
int choose(int distance[], int n, int found[]) // 아직 방문하지 않은 노드들 중 가장 거리가 짧은 노드 선택
{
int i, min, minpos;
min = INT_MAX;
minpos = -1;
for (i = 0; i<n; i++)
if (distance[i]< min && !found[i]) {
min = distance[i];
minpos = i;
}
return minpos;
}
void print_status(GraphType* g)
{
// static int step=1;
// printf("STEP %d: ", step++);
// printf("distance: ");
for (int i = 0; i < g->n; i++) {
if (distance[i] == INF)
printf(" * ");
else
printf("%2d ", distance[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf(" found: ");
for (int i = 0; i<g->n; i++)
printf("%2d ", found[i]);
printf("\n\n");
}
void print_path(int start, int end) // 뒤에서부터 출력하기 위해 재귀로 구현
{
int u = end ;
if(start == end) {
printf("%d -> ", start);
return;
}
else {
print_path(start, previous[u]);
printf("%d -> ", u);
}
}
//
void shortest_path(GraphType* g, int start)
{
int i, u, w;
for (i = 0; i<g->n; i++) /* 초기화 */
{
distance[i] = g->weight[start][i];
found[i] = FALSE;
previous[i] = start;
}
found[start] = TRUE; /* 시작 정점 방문 표시 */
distance[start] = 0;
for (i = 0; i<g->n-1; i++) {
u = choose(distance, g->n, found);
found[u] = TRUE;
print_path(start, u);
printf("<%d>\n", distance[u]);
for (w = 0; w<g->n; w++){
if (!found[w]){
if (distance[u] + g->weight[u][w] < distance[w]){
distance[w] = distance[u] + g->weight[u][w];
previous[w] = u;
}
}
}
}
}
// 그래프 초기화
void graph_init(GraphType *g)
{
// 구현
g->n = 0;
for(int i=0; i<MAX_VERTICES; i++){
for(int j=0; j<MAX_VERTICES; j++){
if(i == j){
g->weight[i][j] = 0;
} else {
g->weight[i][j] = INF;
}
}
}
}
void insert_edge(GraphType *g, int start, int end, int key)
{
if( start >= g->n || end >= g->n ){
fprintf(stderr,"그래프 : 정점 번호 오류");
return;
}
// ƒ⁄µÂ ª¿‘
g->weight[start][end] = key;
g->weight[end][start] = key;
}
/* */
void read_graph(GraphType *g, char *filename)
{
// 구현
int number, u, v, key;
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen(filename, "rt");
if (fp == NULL)
{
printf("file %s open error!\n", filename);
return;
}
fscanf(fp, "%d\n", &number);
g->n = number;
// 구현: while (fscanf(fp, "%d\n", &n) != EOF) {...} 을 사용한다.
while(fscanf(fp, "%d\n", &u) != EOF && fscanf(fp, "%d\n", &v) != EOF && fscanf(fp, "%d\n", &key) != EOF){
insert_edge(g, u, v, key);
}
fclose(fp);
}
int main(void)
{
GraphType g;
graph_init(&g);
read_graph(&g, "input.txt");
shortest_path(&g, 4);
return 0;
}
4) 시작 정점부터 경로를 출력하기 위해 previous[u]라는 배열을 하나 더 선언하였다.
previous[u] = u 전의 노드이다.
void print_path(int start, int end) // 뒤에서부터 출력하기 위해 재귀로 구현
{
int u = end ;
if(start == end) {
printf("%d -> ", start);
return;
}
else {
print_path(start, previous[u]);
printf("%d -> ", u);
}
}
//
void shortest_path(GraphType* g, int start)
{
int i, u, w;
for (i = 0; i<g->n; i++) /* 초기화 */
{
distance[i] = g->weight[start][i];
found[i] = FALSE;
previous[i] = start;
}
found[start] = TRUE; /* 시작 정점 방문 표시 */
distance[start] = 0;
for (i = 0; i<g->n-1; i++) {
u = choose(distance, g->n, found);
found[u] = TRUE;
print_path(start, u);
printf("<%d>\n", distance[u]);
for (w = 0; w<g->n; w++){
if (!found[w]){
if (distance[u] + g->weight[u][w] < distance[w]){
distance[w] = distance[u] + g->weight[u][w];
previous[w] = u;
}
}
}
}
}
: 처음에 previous 배열을 모두 start로 초기화시켜준다.
: 그리고 노드를 하나씩 정해갈 때마다 previous[u]값을 설정한다.
: print_path에서 재귀를 통해 뒤에서부터 출력한다.
5) 시간 복잡도
: O(n^2)
3. 플로이드 알고리즘 - 최단경로
1) 작동 방식
: 모든 정점 사이의 최단 경로를 찾는다.
: (i 에서 j로 가는 거리)와 (i -> k + k ->j 로 가는 거리) 중에 더 짧은 경로로 간다.

2) 전체 코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAX_VERTICES 100
#define INF 1000000 /* 무한대 (연결이 없는 경우) */
typedef struct GraphType {
int n; // 정점의 개수
int weight[MAX_VERTICES][MAX_VERTICES];
} GraphType;
int A[MAX_VERTICES][MAX_VERTICES];
void printA(GraphType *g)
{
int i, j;
printf("===============================\n");
for (i = 0; i<g->n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j<g->n; j++) {
if (A[i][j] == INF)
printf(" * ");
else printf("%3d ", A[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("===============================\n");
}
void floyd(GraphType* g)
{
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i<g->n; i++)
for (j = 0; j<g->n; j++)
A[i][j] = g->weight[i][j];
printA(g);
for (k = 0; k<g->n; k++) {
for (i = 0; i<g->n; i++)
for (j = 0; j<g->n; j++)
if (A[i][k] + A[k][j] < A[i][j])
A[i][j] = A[i][k] + A[k][j];
printA(g);
}
}
int main(void)
{
GraphType g = { 7,
{{ 0, 7, INF, INF, 3, 10, INF },
{ 7, 0, 4, 10, 2, 6, INF },
{ INF, 4, 0, 2, INF, INF, INF },
{ INF, 10, 2, 0, 11, 9, 4 },
{ 3, 2, INF, 11, 0, INF, 5 },
{ 10, 6, INF, 9, INF, 0, INF },
{ INF, INF, INF, 4, 5, INF, 0 } }
};
floyd(&g);
return 0;
}
3) 시간 복잡도
O(n^3)
- 다익스트라 알고리즘도 모든 정점부터 시작하는 최단 경로를 구하려면 O(n^2)을 n번 반복해야 하기 때문에
시간복잡도가 O(n^3)가 된다.
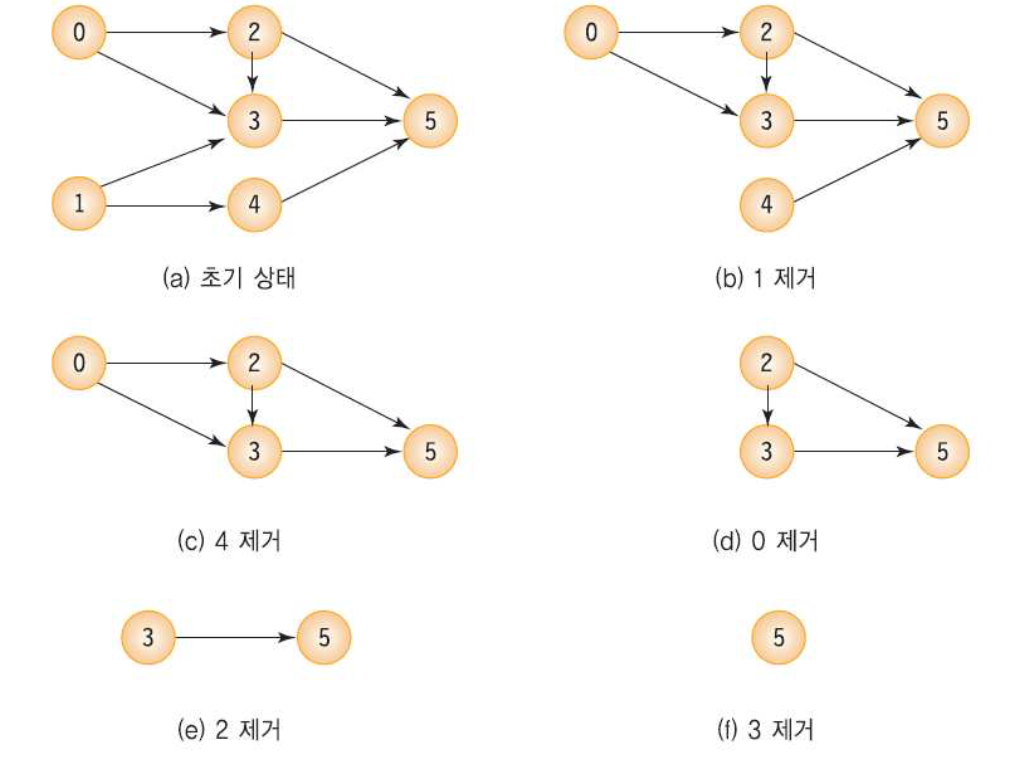
4. 위상 정렬
: 방향이 있는 그래프에서 선행 순서를 위배하지 않으면서도 모든 정점을 방문하는 알고리즘이다.
1) 동작 방식
: 선수 노드가 없는 노드를 선택한다.
: 선택한 노드의 선행 관계를 삭제한다.
: 선택되지 않은 노드들 중 선수 노드가 없는 노드를 다시 선택한다.
x 모든 정점이 선택될 때까지 반복

2) 전체 코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAX_VERTICES 50
typedef struct GraphNode
{
int vertex;
struct GraphNode *link;
} GraphNode;
typedef struct GraphType {
int n; // 정점의 개수
GraphNode *adj_list[MAX_VERTICES];
} GraphType;
// 그래프 초기화
void graph_init(GraphType *g)
{
int v;
g->n = 0;
for (v = 0; v<MAX_VERTICES; v++)
g->adj_list[v] = NULL;
}
// 정점 삽입 연산
void insert_vertex(GraphType *g, int v)
{
if (((g->n) + 1) > MAX_VERTICES) {
fprintf(stderr, "그래프: 정점의 개수 초과");
return;
}
g->n++;
}
// 간선 삽입 연산, v를 u의 인접 리스트에 삽입한다.
void insert_edge(GraphType *g, int u, int v)
{
GraphNode *node;
if (u >= g->n || v >= g->n) {
fprintf(stderr, "그래프: 정점 번호 오류");
return;
}
node = (GraphNode *)malloc(sizeof(GraphNode));
node->vertex = v;
node->link = g->adj_list[u];
g->adj_list[u] = node;
}
#define MAX_STACK_SIZE 100
typedef int element;
typedef struct {
element stack[MAX_STACK_SIZE];
int top;
} StackType;
// 스택 초기화 함수
void init(StackType *s)
{
s->top = -1;
}
// 공백 상태 검출 함수
int is_empty(StackType *s)
{
return (s->top == -1);
}
// 포화 상태 검출 함수
int is_full(StackType *s)
{
return (s->top == (MAX_STACK_SIZE - 1));
}
// 삽입함수
void push(StackType *s, element item)
{
if (is_full(s)) {
fprintf(stderr, "스택 포화 에러\n");
return;
}
else s->stack[++(s->top)] = item;
}
// 삭제함수
element pop(StackType *s)
{
if (is_empty(s)) {
fprintf(stderr, "스택 공백 에러\n");
exit(1);
}
else return s->stack[(s->top)--];
}
// 위상정렬을 수행한다.
int topo_sort(GraphType *g)
{
int i;
StackType s;
GraphNode *node;
// 모든 정점의 진입 차수를 계산
int *in_degree = (int *)malloc(g->n * sizeof(int));
for (i = 0; i < g->n; i++) // 초기화
in_degree[i] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < g->n; i++) {
GraphNode *node = g->adj_list[i];//정점 i에서 나오는 간선들
while (node != NULL) {
in_degree[node->vertex]++;
node = node->link;
}
}
// 진입 차수가 0인 정점을 스택에 삽입
init(&s);
for (i = 0; i < g->n; i++) {
if (in_degree[i] == 0) push(&s, i);
}
// 위상 순서를 생성
while (!is_empty(&s)) {
int w;
w = pop(&s);
printf("정점 %d ->", w); //정점 출력
node = g->adj_list[w]; //각 정점의 진입 차수를 변경
while (node != NULL) {
int u = node->vertex;
in_degree[u]--; //진입 차수를 감소
if (in_degree[u] == 0) push(&s, u);
node = node->link; // 다음 정점
}
}
free(in_degree);
printf("\n");
return (i == g->n); // 반환값이 1이면 성공, 0이면 실패
}
//
int main(void)
{
GraphType g;
graph_init(&g);
insert_vertex(&g, 0);
insert_vertex(&g, 1);
insert_vertex(&g, 2);
insert_vertex(&g, 3);
insert_vertex(&g, 4);
insert_vertex(&g, 5);
//정점 0의 인접 리스트 생성
insert_edge(&g, 0, 2);
insert_edge(&g, 0, 3);
//정점 1의 인접 리스트 생성
insert_edge(&g, 1, 3);
insert_edge(&g, 1, 4);
//정점 2의 인접 리스트 생성
insert_edge(&g, 2, 3);
insert_edge(&g, 2, 5);
//정점 3의 인접 리스트 생성
insert_edge(&g, 3, 5);
//정점 4의 인접 리스트 생성
insert_edge(&g, 4, 5);
//위상 정렬
topo_sort(&g);
// 동적 메모리 반환 코드 생략
return 0;
}
'Computer Science > Data Structure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [문제해결기법01] 순환(재귀) recursion (0) | 2021.04.07 |
|---|---|
| 자료구조 4 탐색 (0) | 2020.12.10 |
| 자료구조 3 - 3) 그래프 MST : 크루스칼, 프림 (0) | 2020.12.05 |
| 자료구조 3 - 2) 그래프 BFS, DFS (0) | 2020.12.05 |
| 자료구조 3 - 1) 그래프 (0) | 2020.12.04 |